Pen CS will be opening up the full capability of PAT CAT though a purpose built API.
Taking Your Population Health Reporting to the Next Level
The PAT BI database provides unprecedented access to the data derived and submitted from CAT4 to your PAT CAT. A purpose built granular database designed for use with Business Intelligence (BI) Tools such as Qlik, Power BI etc. empowers your PHN/ACCHO to explore the depth of data currently at your disposal. Practice data is stored at patient level with an encrypted unique patient identifier allowing for comprehensive longitudinal reporting.
KEY FEATURES
- Uninterrupted access to your data
- Granular patient level database structure
- Fully documented database schema
- Includes PAT CAT database cleaning tools and services
- Capacity for patient and practice longitudinal reporting
- If you are using the Pen CS Geocoding Service you will have the added advantage of bringing together your practices CAT4 clinical data with additional data sets using the exposed Statistical Area 2 (SA2) codes. Each patient, in CAT4, has their address mapped to a SA2 code. Once an SA2 code is assigned to a patient, it can be linked to data sets available outside of the practice clinical information system such as immunisation rates and ABS data.
PAT BI Database Server Specifications
| Minimum Requirements | Recommended Requirements |
|---|---|---|
Operating System | Windows Server 2012 (Standard/R2) X64 or higher |
|
Processor | 8 Logical Cores | 32 Logical Cores or more |
RAM | 16 GB | 64 GB or more |
Hard Disk | 500 GB* | 1 TB* or more |
Microsoft .NET | .NET 3.5, 4.5 and 4.6.1 |
|
Database | Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Standard Edition | Microsoft SQL Server 2016 Standard Edition |
Other Requirements |
|
|
Operational Requirements |
maintain the database and the server
database (including related artifacts) and the server |
|
* Refer to the Estimated Database Size Growth table.
Estimated Database Size Growth
Patients per Extract | Total Practices | Total Duration of Submission (months) | Total Patients for the Duration | Estimated Size (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
12,000 | 250 | 3 | 9,000,000 | 140 |
12,000 | 250 | 6 | 18,000,000 | 279 |
12,000 | 250 | 9 | 27,000,000 | 419 |
12,000 | 250 | 12 | 36,000,000 | 558 |
12,000 | 250 | 15 | 45,000,000 | 698 |
12,000 | 250 | 18 | 54,000,000 | 837 |
12,000 | 250 | 21 | 63,000,000 | 977 |
12,000 | 250 | 24 | 72,000,000 | 1,116 |
12,000 | 250 | 27 | 81,000,000 | 1,256 |
12,000 | 250 | 30 | 90,000,000 | 1,395 |
12,000 | 250 | 33 | 99,000,000 | 1,535 |
12,000 | 250 | 36 | 108,000,000 | 1,674 |
12,000 | 250 | 39 | 117,000,000 | 1,814 |
12,000 | 250 | 42 | 126,000,000 | 1,953 |
12,000 | 250 | 45 | 135,000,000 | 2,093 |
12,000 | 250 | 48 | 144,000,000 | 2,232 |
12,000 | 250 | 51 | 153,000,000 | 2,372 |
12,000 | 250 | 54 | 162,000,000 | 2,511 |
12,000 | 250 | 57 | 171,000,000 | 2,651 |
12,000 | 250 | 60 | 180,000,000 | 2,790 |
12,000 | 250 | 63 | 189,000,000 | 2,930 |
12,000 | 250 | 66 | 198,000,000 | 3,069 |
12,000 | 250 | 69 | 207,000,000 | 3,209 |
12,000 | 250 | 72 | 216,000,000 | 3,348 |
12,000 | 250 | 75 | 225,000,000 | 3,488 |
12,000 | 250 | 78 | 234,000,000 | 3,627 |
12,000 | 250 | 81 | 243,000,000 | 3,767 |
12,000 | 250 | 84 | 252,000,000 | 3,906 |
12,000 | 250 | 87 | 261,000,000 | 4,046 |
12,000 | 250 | 90 | 270,000,000 | 4,185 |
"Estimated Size (GB) =((Patients Per Extract ×Total Practices ×Total Duration)/1,000,000)×15.50
Complex Database Storage
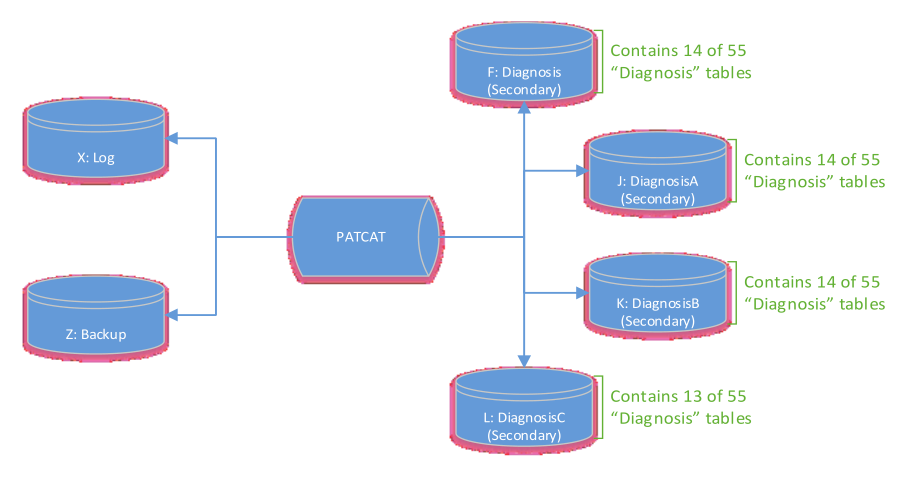
Data growth will eventually hit a limit where increasing disk space is no longer possible. In order to solve the limit issue, we can split the data into multiple drives. Splitting data over multiple disk increases performance of read and writes operations as this spreads the I/O loads, allowing for parallel queries and specific backup/restore of data.
When a drive reach its storage limit, it’s possible to split the data into multiple drives. An example (below) shows the Diagnosis split into 4 disks (other secondary tables has been omitted).
Important: Splitting data into multiple disk incurs a maintenance overhead and complexity in backups, they should be reviewed when splitting data into multiple disks. We recommend having an experienced database administrator to maintain the database and the server. The PHN holds the sole responsibility to protect and/or manage the database (including related artifacts) and the server
Large databases are the domain of a DBA/System engineer for a large database. The below items form the basis of the decision that a DBA/System engineer will need to make as the database grows. These include but are not limited to:
• Data Disk o Quality SSD etc
|
|
|
• Backup/
| • Maintenance Plan
| • Monitoring
|
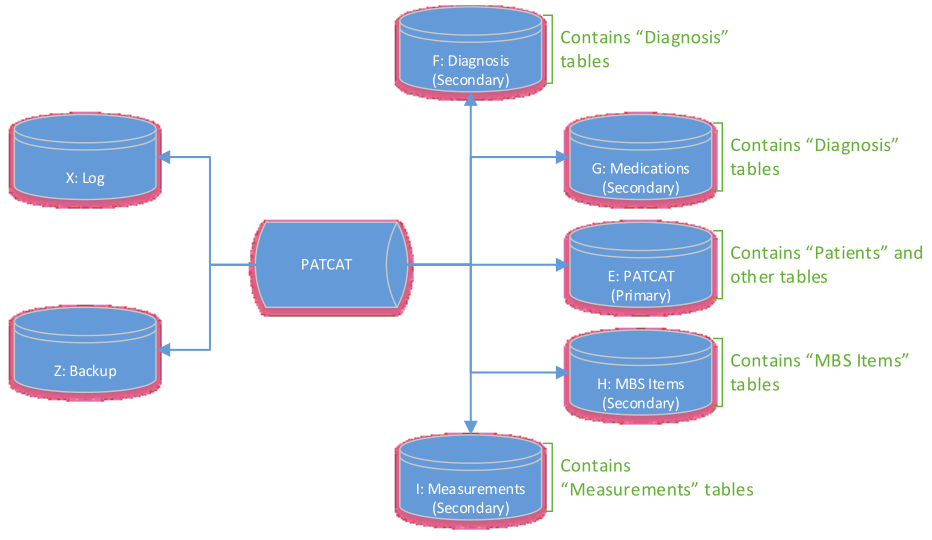
In addition to the PAT BI Database you also get a detailed Database Schema document that will explain exactly how the database tables are connected to each other. Below is s sample template of the PAT BI Database Schema,
Medication_Hormone_Replacement_Therapy_Oestrogen_Only |
|
|
|
Active | bit | Yes | The status of 'Hormone Replacement Therapy Oestrogen Only'.
|
End_Date | datetime | Yes | The end date and time of 'Hormone Replacement Therapy Oestrogen Only' |
ExtractID | bigint | No | The reference identifier of an extract. Use this column to query data for an extract or collection of extracts |
ID | bigint | No | The primary key and seed |
PatientID | bigint | No | The reference identifier of the patient. Use this column to query data for a patient or collection of patients |
Prescription_Date | datetime | Yes | The date and time of the prescription |