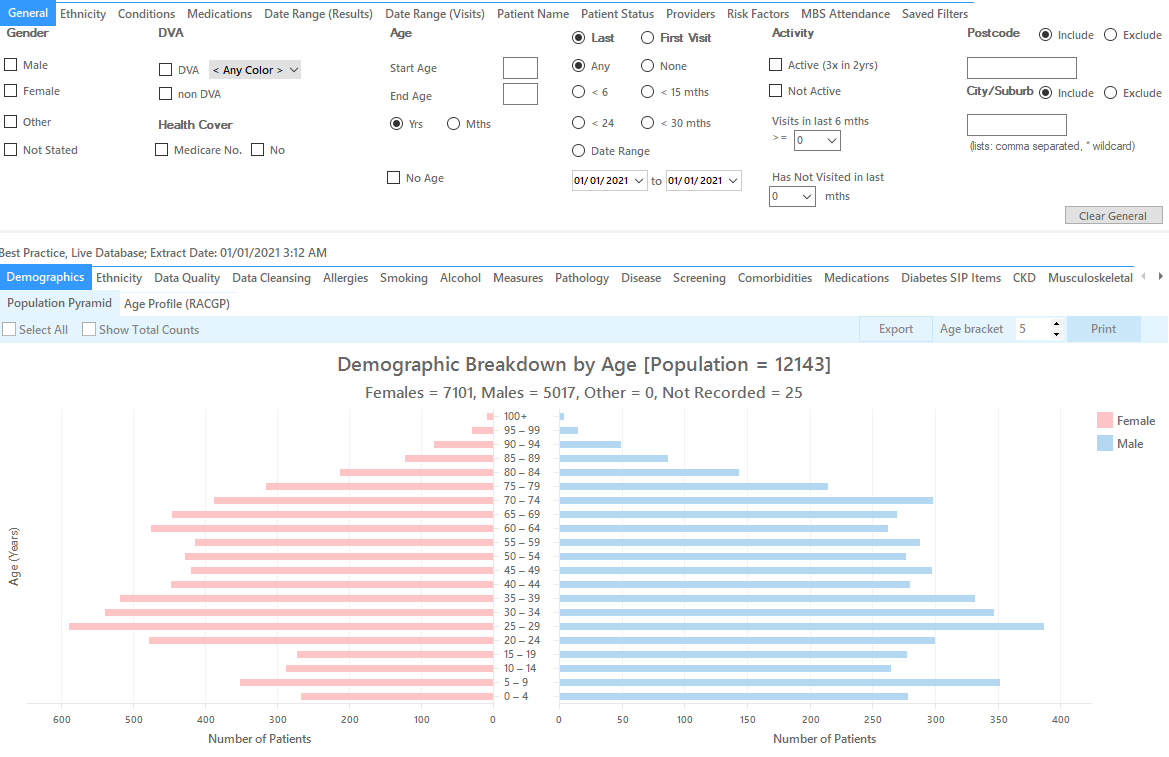
Recipe Name: | Identify all active patients with at least one chronic condition who are eligible for a Medication Review |
Rationale: | Patients with chronic conditions often are taking multiple medications and would benefit from a review of their medications. This will ensure appropriate medications are prescribed and helps to reduce side effects and other medication related risks. |
Target: | To identify active patients with a chronic condition and five or more medications who would benefit from a Home Medication Review (DMMR). |
CAT Starting Point: |
|
CAT Starting Point:
CAT Open - "CAT4" view (all reports) loaded
Population Extract Loaded and Extract Pane "Hidden"
Filter Steps
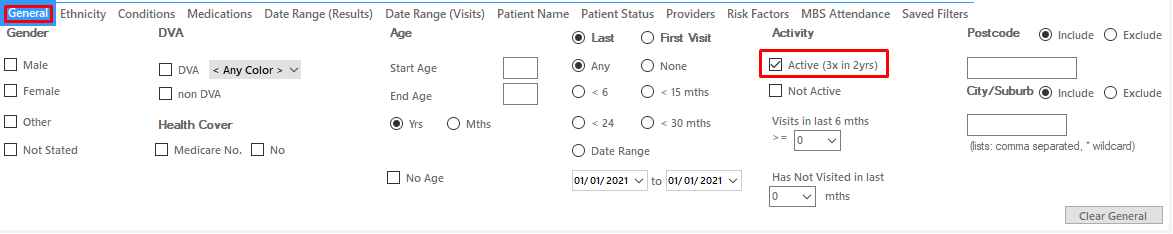
On the "General" tab under Activity select "Active (3x in 2yrs)
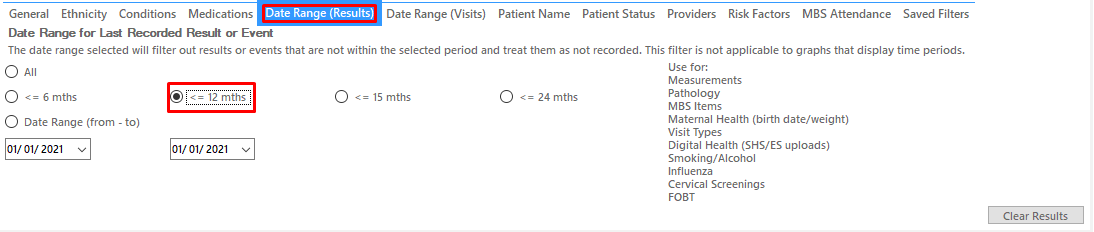
On the "Date Range (Results)" Tab select "12 mths" or another date range
Click 'Recalculate' and 'Hide Filters'
Report Steps
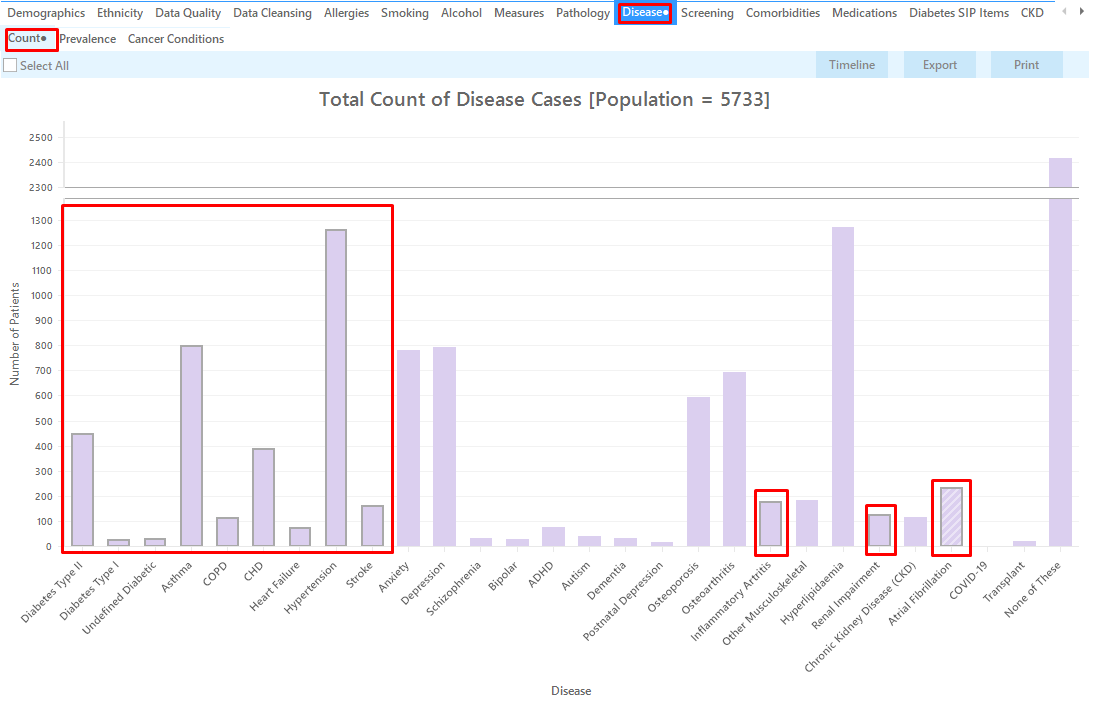
Select 'Disease' tab 'Count'
Click on the "Diabetes Type II, Diabetes Type I, Undefined Diabetes, Asthma, COPD, CHD, Heart Failure, Hypertension, Stroke, Inflammatory Arthritis, Renal Impairment, Atrial Fibrillation" segments of the graph
Any combination of chronic conditions can be selected, this will show all patients with at least one of the selected conditions
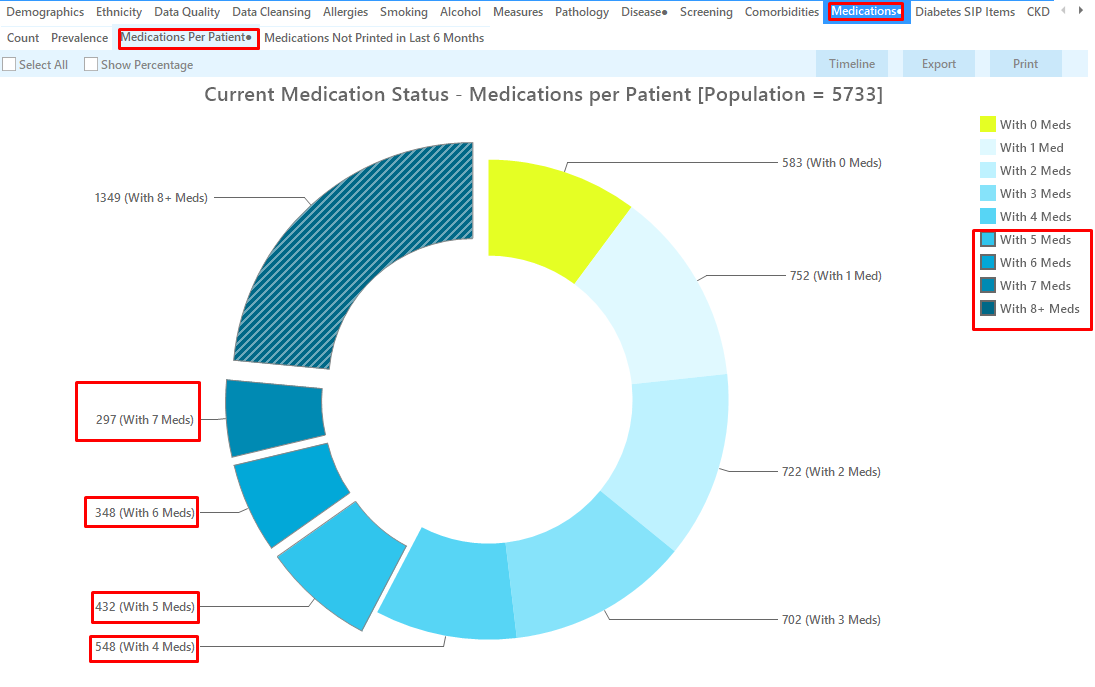
Select the 'Medications' tab 'Medications per Patient'
Click on the "'with 5 meds', 'with 6 meds', 'with 7 meds' and 'with 8+ meds'" segments of the graph
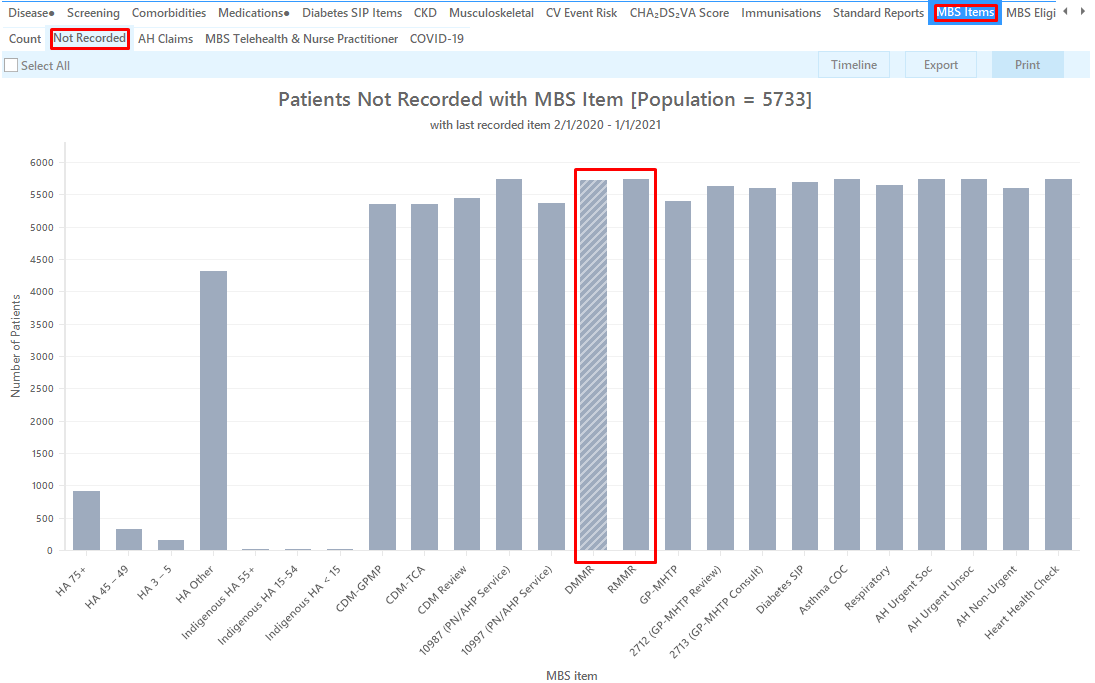
Select the 'MBS Items' tab 'Not recorded'
Click on the "'900 (DMMR)' or '903 (RMMR)'" segments of the graph
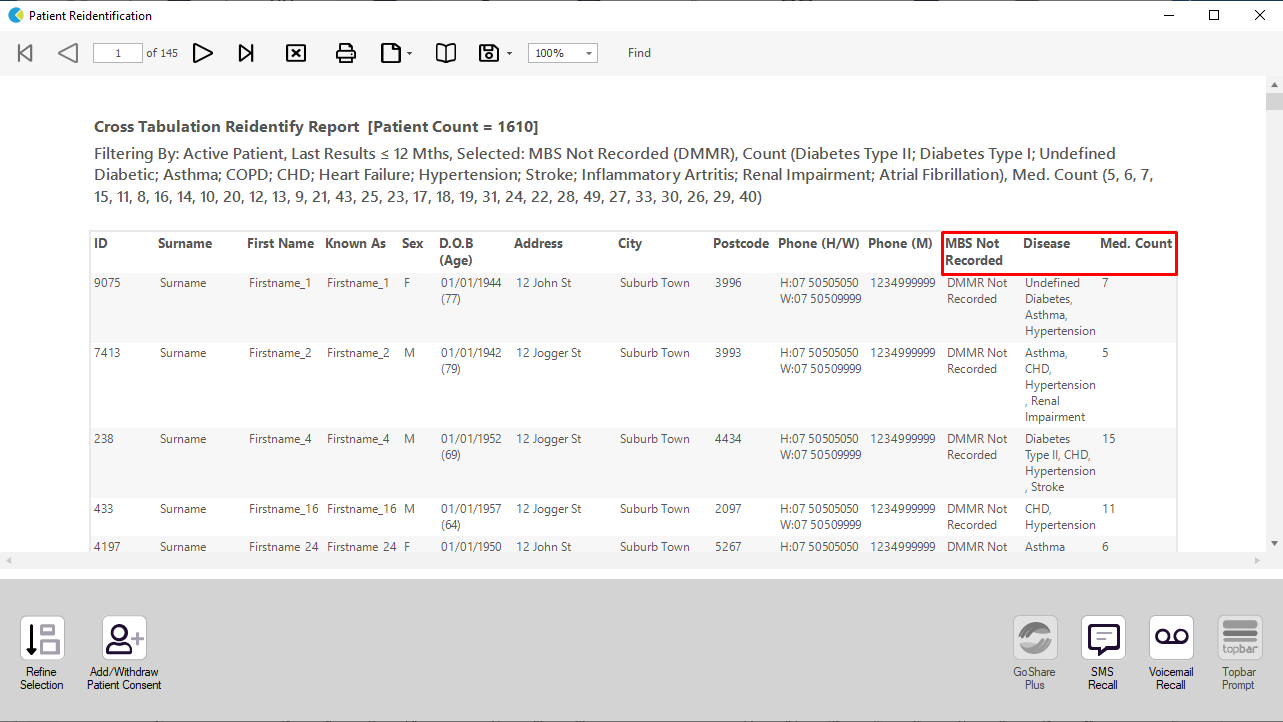
Click on the 'Report' icon on top of the screen to cross-tabulate all selected report views to see the list of patients selected
This will display a list of all patients for whom the selected MBS item has not been claimed in the last 12 months.
The last three columns show disease, medication count and the date of the last claim or simply "not recorded" if the items has never been claimed in your practice.
To Export Patient List to Microsoft Excel:
1. Click on the “Export Icon” at the top of the Patient Reidentification window.
2. Click on “Excel”
3. Choose a file name and a location to save to (eg. Create a folder C:/ClinicalAudit/CAT Patient FollowUp)
4. Click “Save”
The steps above will produce a list of patients with contact details in MS Excel which can then be used to:
1. Go back through the individual patient records in the GP Clinical Desktop System (CDS) and update known records
2. Phone patients to update their record
3. Produce a mail merge to recall patients for follow up
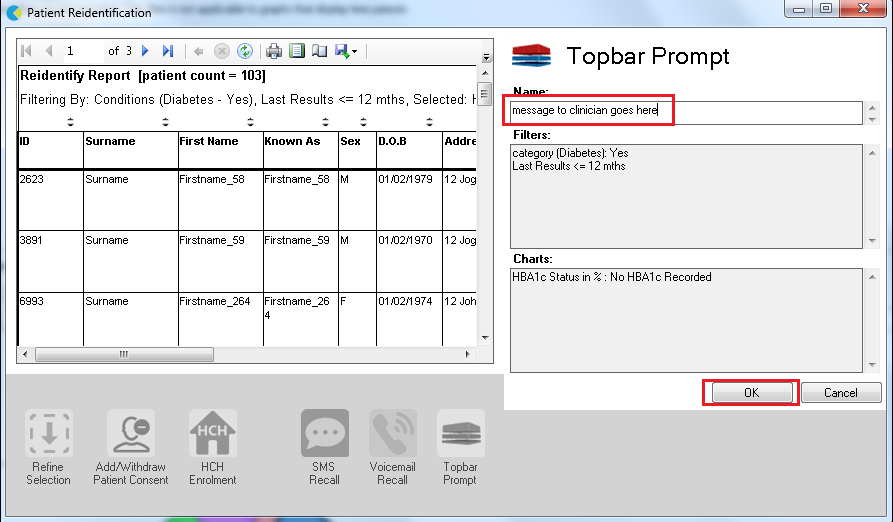
Create a prompt to display in Topbar Remember you need to be in the CAT4 Daily View to be able to create prompts. Other pre-requisites are: To start click on the 'Daily View' icon on the top of your CAT4 screen: Once you have applied the filter(s) and displayed the patients of interest as described above, you can create a prompt that will be shown to all clinicians using Topbar if a patient meeting the prompt criteria is opened in their clinical system. The full guide is available at CAT PLUS PROMPTS and a short guide on how to create prompts in CAT4 can be found at Creating a Prompt in CAT4 To start you have to use the drop-down menu at the bottom of the patient details report and select "Prompt at Consult - Topbar" then click on "Go" to give the new prompt a name. The name you enter is the prompt text displayed in Topbar, so choose a simple but clear name that tells the clinician seeing the prompt what should be done.