Overview
The CAT Childhood Schedule tab provides:
- A graph which displays a child's immunisation status
- A worksheet which details the number of doses of each immunisation that have been received for each child
The NKPI Essential Immunisations tab shows which children are up to date for the immunisations HepB, DTPa, Hib, IPV and MMR for ages 1,2 and 5 only. It also offers the same worksheet as the general childhood schedule graph.
The CAT Age filter allows filtering by age in months as well as years. This can be used to target specific child age groups and determine children that have not received all their immunisations.
The tables at the end of this guide provide information about:
- The immunisations included (Table 1)
- The number of doses required by age (Table 2)
- The additional rules considered to determine status (Table 3). The rules for each immunisation determine whether it is up to date, due or overdue.
A child's overall status will take the 'worst' status of all immunisations given i.e. if any immunisation is overdue the child's overall status will be overdue.
References
The following documents have been referenced:
- The Childhood Immunisation Schedule is provided by the National Immunisation Program Schedule
- The Australian Childhood Immunisation Register (ACIR) Due and Overdue rules available at http://www.medicareaustralia.gov.au/provider/pubs/program/acir.jsp
Graph
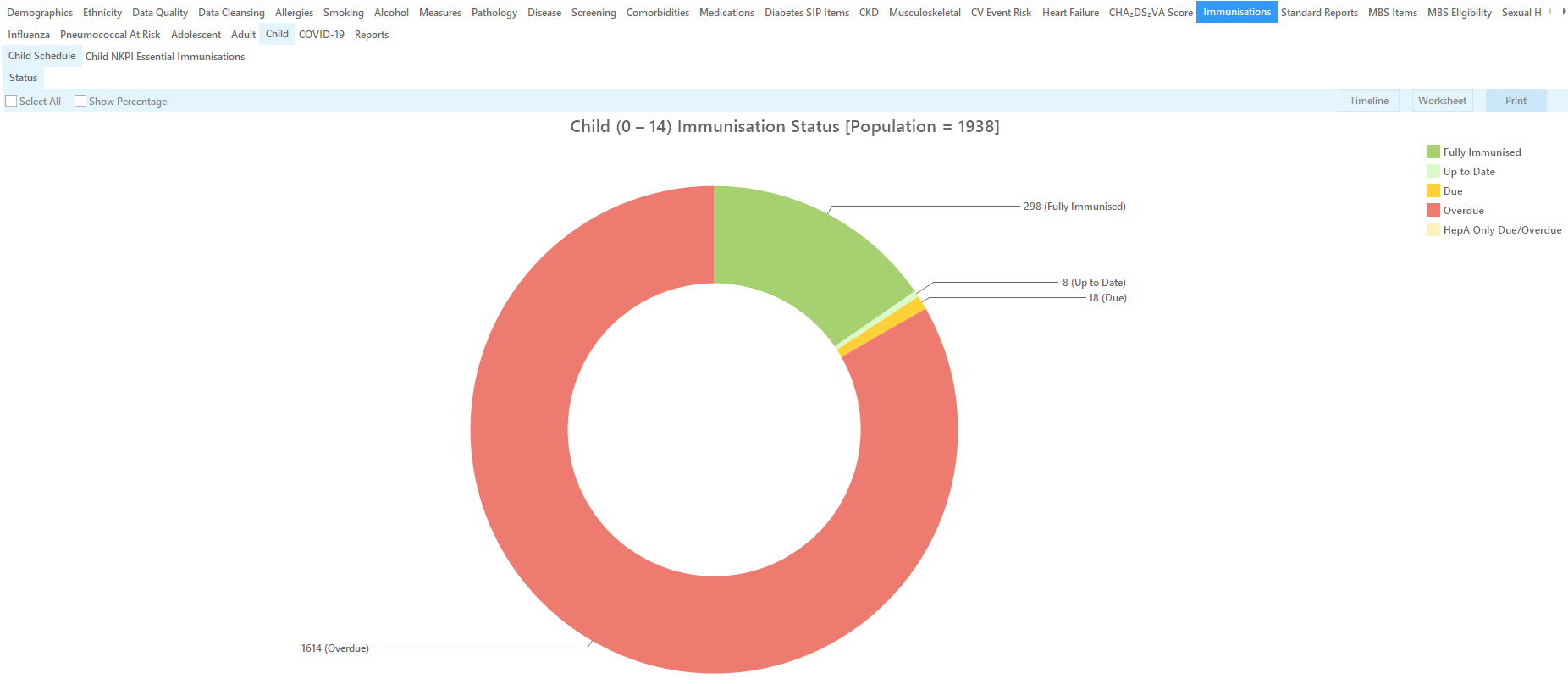
The Immunisations > Child Schedule tab provides a pie chart for children aged 0-7 years with the following status categories:
- Fully immunised – a child has received all the immunisations required for their age (refer Table 2)
- Up to date – a child is not fully immunised but no dose is due (eg. there may be a minimum time period between doses – refer Table 3)
- Due – immunisations are due now
- Overdue – immunisations are overdue
- HepA only Due/Overdue - all immunisations are up to date except HepA
- Overdue and Declined - immunisations are overdue but has been declined by the patient/parents
Worksheet
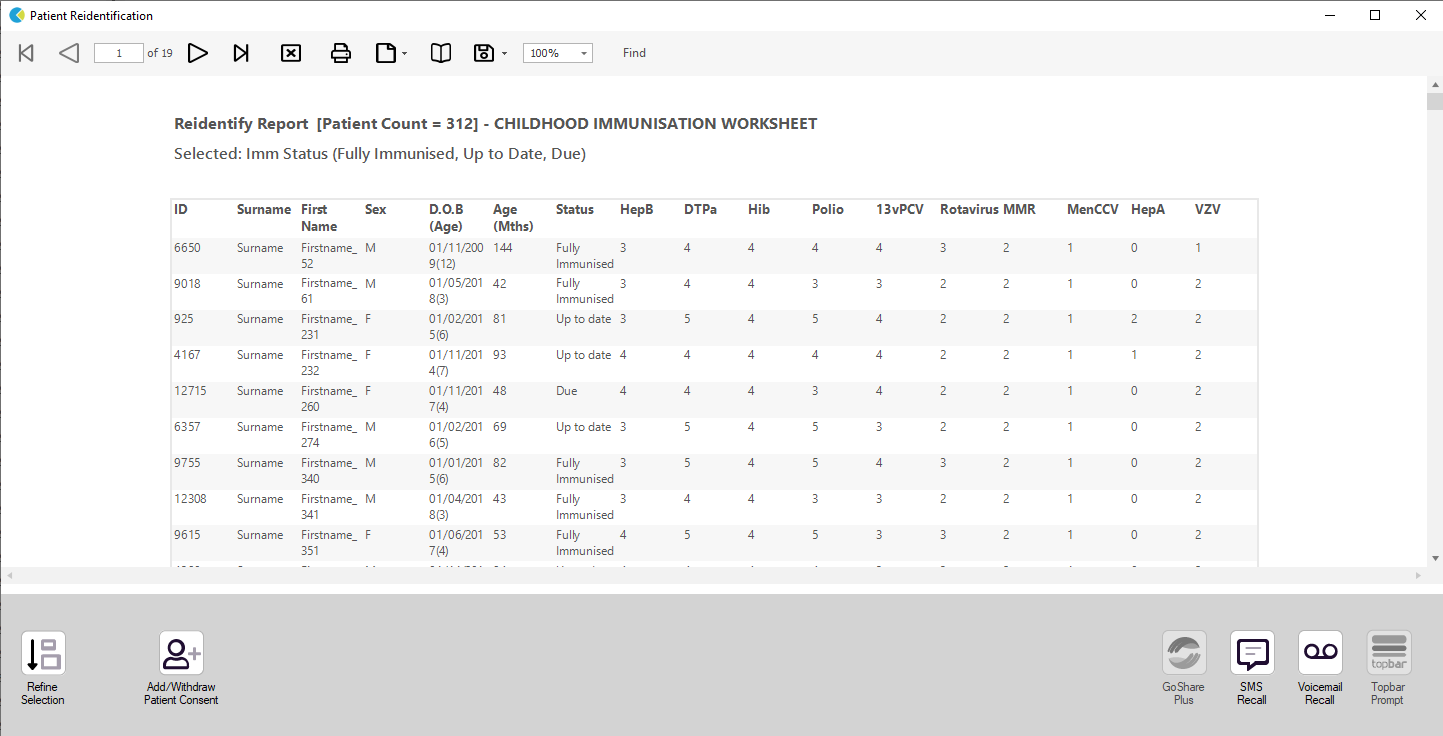
The worksheet button provides a list of patients with the following details:
- age in months
- immunisation status
- number of doses per immunisation
The worksheet is an aid to help the practice to find children who are not up to date and identify which immunisations are still required. As the vaccination pathways for different vaccine brands can differ the practice should check patient records where a child is listed as due or overdue. In the worksheets the overdue immunisation(s) will be displayed with a * next to the current count to assist in identifying the reason for the child being listed as overdue
Table 1: Immunisation list for children
Hep B | Hepatitis B |
DTPa | Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (acellular pertussis) |
DTPa-HB-IPV-Hib | Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (acellular pertussis), Hepatitis B, Polio, Haemophilus influenzae type B |
DTpa-IPV | Diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough (acellular pertussis) Polio |
Hib | Haemophilus influenzae type B |
Rotavirus | Rotavirus |
Meningococcal ACWY | Meningococcal ACWY |
Meningococcal B | Meningococcal B |
MMR | Measles, mumps and Rubella |
MMRV | Measles, mumps, Rubella and Varicella (Chicken Pox) |
Hep A (ATSI children WA, NT, SA, QLD) | Hepatitis A |
20vPCV | Pneumococcal conjugate |
Influenza (children with specific medical conditions) | Influenza |
Table 2: Immunisation total recommended doses by age
This table shows the recommended doses for age as provided by the National Immunisation Program Schedule.
Immunisation/Age | Birth | 2 m | 4 m | 6 m | 6 m to ≤ 5 yrs | 12 m | 18 m | 4 yrs |
Hep B | 1+ | |||||||
DTPa | 1 | |||||||
DTPa-IPV | 1 | |||||||
DTPa- HB-IPV-Hib | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||
Rotavirus | 1 | 1 | ||||||
Meningococcal ACWY | 1 | |||||||
Meningococcal B | 1* | 1* | 1# | 1* | ||||
MMR | 1 | |||||||
MMRV | 1 | |||||||
Hep A | 1& | 1& | ||||||
Hib | 1 | |||||||
20vPCV | 1 | 1 | 1# | 1 | 1& | |||
Influenza | 1^ |
*ATSI children + usually offered in hospital
# ATSI and specific medical conditions & ATSI children in WA,NT,SA and
^ annually Qld
A child's age in months determines how many doses of each immunisation should have been received. For example, by age 6 months a child should have had 3 doses of DTPa.
The number of doses for age will differ between States and Territories due to the needs of geographic and demographic conditions.
Table 3: Immunisation Due and Overdue rules based on 'The Australian Childhood Immunisation Register (ACIR) Due and Overdue rules'
Immunisation | Dose | Additional Criteria to determine if status = Up to date | Status | ||
Up to date | Due | Overdue | |||
HepB - Birth | 1 | Child age > 7days* | In first 7 days | ||
HepB | 1 | 2 months | 3 months | ||
2 | Last dose | 4 months | 5 months | ||
3 | Last dose | 6 months | 7 months | ||
DTPa | 1 | 2 months | 3 months | ||
2 | Last dose | 4 months | 5 months | ||
3 | Last dose | 6 months | 7 months | ||
4 | Last dose | 18 months | 19 months | ||
| 5 | Last dose given< 6months | 48 months | 49 months | ||
Hib | 1 | Dose 1 > 15months | 2 months | 3 months | |
2 | Dose 2 > 15months | Last dose | 4 months | 5 months | |
3 | Dose 3 >15months | Last dose | 6 months | 7 months | |
4 | Last dose | 18 months | 19 months | ||
IPV | 1 | 2 months | 3 months | ||
2 | Last dose | 4 months | 5 months | ||
3 | Dose 3 > 48months | Last dose | 6 months | 7 months | |
4 | Last dose | 48 months | 49 months |
Pneumococcal conjugate | 1 | Dose 1 > 17months | 2 months | 3 months | |
2 | Dose 2 > 12months | Last dose | 4 months | 5 months | |
3 | Last dose | 6 months | 7 months | ||
Rotavirus | If no dose by 14weeks then no doses due/overdue | ||||
1 | Dose 1 > 28weeks | 2 months | 3 months | ||
2 | Dose 2 > 28weeks | 4 months | 5 months | ||
3 | No doses due/overdue > 32weeks | 6 months | 7 months | ||
MMR - DOB < 1/1/2012 | 1 | 12 months | 13 months | ||
2 | 48 months | 49 months | |||
MMR - DOB >= 1/1/2012 | 1 | 12 months | 13 months | ||
2 | 18 months | 19 months | |||
MenCCV | 1 | Imm can be given in more than 1 dose – a dose must exist after 12months* | 12 months | 13 months | |
HepA Strait Islander) | 1 | 2 doses are due in the second year of life* | 12 months | 25 months | |
2nd dose for high risk areas | 2 | 18 months | 25 months | ||
VZV | 1 | 18 months | 19 months | ||
23vPPV | 1 | 18 months | 19 months |